Home Ventilation and Eco Heating Systems
Ventilation
The average person normally consumes about 15,000 litres of air each day, of which, up to 90% may consist of your home’s indoor air. To achieve a constant level of fresh clean air throughout your home for you and your family you will need to replace your home’s air every two hours.
An effective ventilation system within your home will protect the building, belongings and occupants against potentially harmful build-
Heat Recovery
A heat ventilation recovery system is not a heating or cooling system but a fresh air ventilation system that filters and replenishes your homes air with air from outside.
The system simply takes the warm air from your home and passes it through an advanced filtration membrane which absorbs heats from the warm air and then transfers the heat to the passing air from outside –
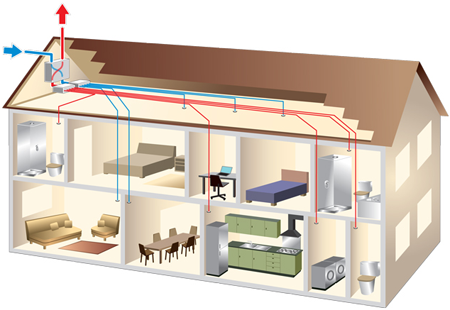
Duplex Vent System
Duplexvent - Effective and Efficient
Heat recovery is a process of continuously preheating incoming cool supply air by warming it with the outgoing exhaust air.
Warm air is not simply exhausted but transfers most of its heat to supply air in a highly efficient heat recovery exchanger. At no time do the airstreams mix as the heat radiates through the plates of the exchanger.
What is Heat Recovery Efficiency?
Heat recovery efficiency is the utilising of waste heat to cool fresh incoming air.
Generally speaking efficiency above 60% is considered good and above 80% excellent.
The heat recovery efficiency for Duplexvent units is up to 90% (it depends on the unit size, air flow and the heat recovery exchanger type). The heat recovery exchanger is fitted directly in the ventilation unit. This allows use of heat recovery in all building types such as flats, apartments, family houses and residential accommodation. Larger units can be installed in commercial buildings, swimming pools, retail and industrial buildings.
Duplexvent units also incorporate a “By-
Heat recovery exchangers can be used even in air-
Fresh Air for a Healthy Environment
For the maintenance of the building fabric and for a healthy indoor climate, controlled mechanical ventilation is essential.
Energy savings are achieved by improved insulating measures and by the use of heat recovery. Carbon emissions in the dwelling are also reduced with the contribution of heat recovery. Just as important is that there is a healthy and comfortable climate in highly insulated buildings.
Research proves that people living, working or studying in inadequately ventilated buildings suffer from more ailments, such as headache and allergies. On average, humans spend 90% of their lives in enclosed buildings. Therefore, it is of prime importance to provide healthier indoor air, free from odours, high humidity and airborne pollutants.
Extract Air
Stale air is contaminated with humidity, toxins and smells extracted from the kitchen, bathroom and toilet.
Outlet grilles in toilets and wet room areas, such as the bathroom, en-
Supply Air
Fresh air is fed directly from outside into the ventilation system through a filter.
The heat taken from the extracted air is used to warm the fresh filtered air in the exchanger and then flows through ducting to termination points such as air valves or air inlets into the living rooms and bedrooms. By undercutting doors and fitting transfer grilles fresh air circulation is ensured throughout the dwelling.